My Garage
My Account
Cart
Genuine Saturn LS1 Starter
Starter Ignition- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
1 Starter found
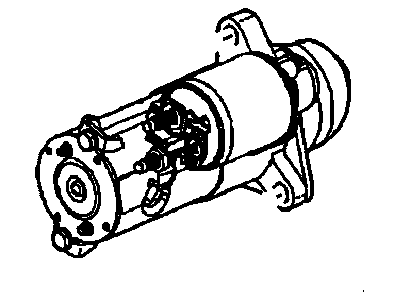
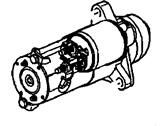
Saturn LS1 Starter Asm, (Remanufacture) (Pg260D)
Part Number: 89017756$303.62 MSRP: $550.31You Save: $246.69 (45%)Ships in 1-2 Business Days
Saturn LS1 Starter
As applied to the Starter in the Saturn LS1 Vehicles, this component plays a critical role of powering the electric energy coming from the battery in a manner that will crank the engine. It employs a solenoid that is externally located with the battery connected that engaging the starter motor. In the starter body, a rotating armature engages field coils or permanent magnet and through electromagnetic force spins the starter drive. Other features available on the system to enhance safety are a neutral safety switch for auto transmissions plus a clutch switch for manual transmissions, thus preventing the engine from starting while in gear. There have been different types of starter used in Saturn LS1 vehicles some of them are gear reduction starters, which engage the drive by way of a reduction gear. OE starters are found snug for standard engines, but may not offer enough cranking torque for high compression motors where kick back may be an issue and therefore high compression motors require a more efficient and durable starter. Modern starter design has advanced than how it was used in the beginning and it has resulted to creation of higher torque and durability aspects especially when used in performance cars.
Each OEM Saturn LS1 Starter we offer is competitively priced and comes with the assurance of the manufacturer's warranty for the part. Furthermore, we guarantee the speedy delivery of your orders right to your doorstep. Our hassle-free return policy is also in place for your peace of mind.
Saturn LS1 Starter Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: How to troubleshoot a malfunction in the Starter on Saturn LS1?A:If you encounter a malfunction in the starting circuit, don't immediately assume that the starter is the issue. Begin by checking the Battery Cable clamps for cleanliness and tightness at the battery connection. Inspect the battery cables and replace any defective ones. Test the battery's condition, and if it fails, replace it. Check the starter solenoid wiring and connections using wiring diagrams. Verify the tightness of the starter mounting bolts. Ensure that the shift lever is in PARK or NEUTRAL (automatic transaxle) or the clutch pedal is pressed (manual transaxle). For vehicles with automatic transaxle, check the adjustment of the Transmission Range (TR) switch, and for manual transaxle, ensure the clutch start switch is correctly installed. If the starter motor doesn't operate when the ignition switch is turned to START, check for voltage to the solenoid using a test light or voltmeter while an assistant turns the ignition switch to START. If voltage is absent, inspect the starting system circuit using wiring diagrams. If voltage is present but the starter doesn't work, remove it from the engine compartment and bench test it. If the starter turns over slowly, perform a starter cranking voltage and current draw test with the starter assembly on the engine. Observe battery voltage and current draw using an amp meter, making sure they stay within the correct range. If not, replace the starter with a new unit. To check the starter/solenoid assembly on the bench, connect jumper cables, apply battery voltage to the solenoid, and observe the movements of the solenoid plunger, shift lever, and pinion drive. Depending on the observations, identify whether the solenoid, starter motor, or starter/solenoid assembly is defective.