My Garage
My Account
Cart
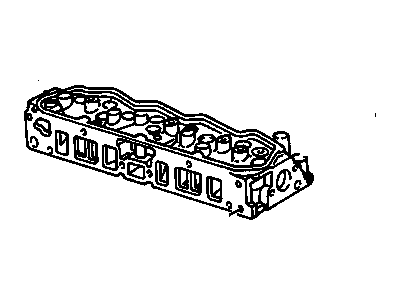
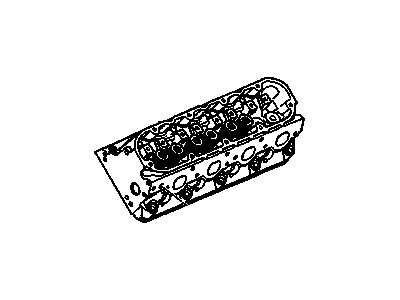
Genuine 1987 Pontiac Fiero Cylinder Head
Head- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
2 Cylinder Heads found
- Product Specifications
- Other Name: Head Kit,Cyl; Cylinder Head
- Item Weight: 48.00 Pounds
- Item Dimensions: 22.8 x 8.7 x 4.6 inches
- Condition: New
- Fitment Type: Direct Replacement
- SKU: 12360340
- Warranty: This genuine part is guaranteed by GM's factory warranty.
- Product Specifications
- Other Name: Head, Cyl
- Item Weight: 29.60 Pounds
- Item Dimensions: 21.2 x 6.6 x 6.7 inches
- Condition: New
- Fitment Type: Direct Replacement
- Require Quantity: 2
- SKU: 14054884
- Warranty: This genuine part is guaranteed by GM's factory warranty.
1987 Pontiac Fiero Cylinder Head
We are your prime source for competitively priced and high-quality OEM 1987 Pontiac Fiero Cylinder Head. We provide you with parts that will allow you to save a lot of money without sacrificing quality. All our OEM parts are backed by the manufacturer's warranty and shipped out at a swift rate.
1987 Pontiac Fiero Cylinder Head Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: What steps should be taken for thorough cleaning and inspection of the cylinder head and valve train components during an engine overhaul on 1987 Pontiac Fiero?A: Washing the cylinder head and all the corresponding valve train components and then examining the same will let you determine how much valve service work will be needed in the course of the engine rebuild. As a first step, they start removing all the gasket material and sealing compound deposits from the head gasket, intake manifold and the exhaust manifold sealing surfaces. Scrub off any accumulated scale around the coolant passage and scrub a bristly wire brush through the oil return aperture. Should be advisable to apply running tap in to each of the threaded hole to wash out corrosion and thread sealant then apply compressed air for the evacuation of debris. Deoxidise the cylinder head retaining bolts and the exhaust and intake manifold stud threads with a die while the rocker arm pivot bolt or stud threads should be wire brushed. Remove the cylinder head and wash it with solvent and then thoroughly dry it using compressed air so as to ensure that there is no moisture in every hole and corner of the cylinder head. That is why chemicals which are reduced in carbon can be helpful when it comes to cleaning but should be employed prudently. Rocker arm shafts shall be cleaned with solvent, and dried to eliminate moisture: The rocker arms, pivot balls and push rods, in addition, the oil passages should be blown through with compressed air. Dip and clean all valve springs, keepers, retainers, shields, and spring seat shims with solvent, are to be dried up and for one valve only so as to avoid the mixing up of the parts. Removal of thick deposits on the valve should be scraped of and the valve heads and stems cleaned using a motorized wire brush while ensuring that the valves are properly arranged. All the rocker arm faces should be checked for pitting, excessive wear and roughness, the pivot contact surface also. Take the pushrod tip and roll on flat surface and look for bending and twist, any bent pushroad should be discarded, inspect for any scuffing or excessive wear. Comprehensive examination of the cylinder head for indications of cracks around the valve seats or in the exhaust ports, indications of coolant leakage etc and then replace the head if there is such. With the straightedge and feeler gauge measure the warpage of the head gasket mating surface, check it with the allowable limits and think of reconditioning when the warpage is within the allowable limits. Check also the valve seat in each combustion chamber for pits, cracks or burn and which will call for reconditioning of cylinder head and valves. The measurements taken were inside diameter of valve guides with small hole gauge and a micrometer, firstly on both ends and the second time at the center and the measurement of the valve stem diameter at the center of the guide wear area. Divide the valve outline by the guide, adding the data obtained to the table, and compare the calculated clearances of the stem diameter and guide diameter of each valve and guide to the specified tolerance. look for indications that they are worn out and require reconditioning or replacement in the form of bell mouth wear in the guides. Stem-to-guide clearance can be determined by placing the dial indicator horizontally at the top of the valve stem and lifting the valve; rocking the valve to and fro will take a reading on the lateral movement. Examine the face of each valve and has to look for the cracks, pits and burned spots while examining the stem for cracks and wear, has to rotate the valve also. Take the measurement of the width of the valve margin on each valve, as a particular valve is required to be replaced, if the margin is below the standard size. It is necessary to examine the end of each valve spring to look for signs of wear, to measure it free length and to compare with the defined earlier limits, that is necessary to remove all springs that are shorter than limits. Place the spring on a flat surface to ensure it is squared to a steel straightedge when small end is on bottom. Check the condition of spring retainers and keepers, wearing or crackling them then replace to minimize more deterioration in the course of operations of the engine. If during the inspection it is observed that the valve components are in poor state and worn beyond the specifications then reassemble the valves back in the cylinder head and refer to the valve servicing guidelines. If no parts which are excessively worn are identified, and further, if the valve faces and seats are still healthy, valve train which is inside the cylinder head is again fit without major works; otherwise, follow the normal cylinder head reassembly process.