My Garage
My Account
Cart
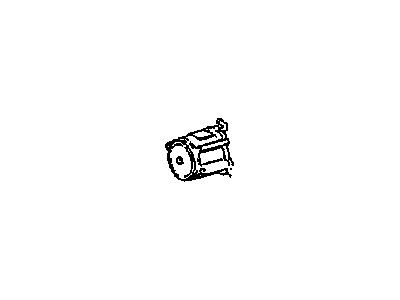
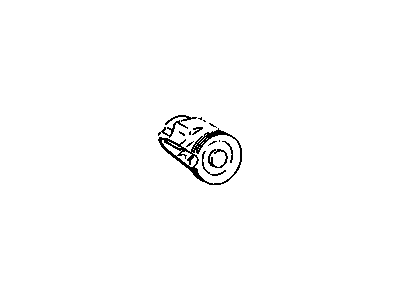
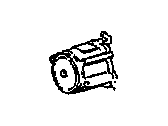
Genuine Buick Century Secondary Air Injection Pump
Secondary Smog Air Injection Pump- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
3 Secondary Air Injection Pumps found
Buick Century Pump Assembly, Secondary Air Injection
Part Number: 12568241$145.22 MSRP: $455.06You Save: $309.84 (69%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysBuick Century Pump Assembly, Air Injector
Part Number: 7842076$116.79 MSRP: $224.60You Save: $107.81 (48%)
Buick Century Secondary Air Injection Pump
Whenever there is consume of fuel in a car, there is always produce of Hydrocarbons (HC) and Carbon Monoxide (CO) among other emitters, and in order to minimize their production in Buick Century vehicles, there is this Secondary Air Injection Pump in the Air Injection Reactor (AIR) system which just blows fresh air into the exhaust system to increase the rate of oxidation of unburned fuel. This system generally comprises of an electric or belt-driven air pump, air control valve and those check valves which help to regulate the air flow depending on the engine temperature and other conditions of operation. This Secondary Air Injection Pump is used in Buick Century models to inject pressurized air into the exhaust ports during engine warm-up then into the catalytic converter at the optimum temperature is attained. This approach benefits in reducing emissions during some phases of the engine operation that is vital for an efficient operation. Further, there are also some safety measure like diverter valves as well as one-way check valves in order to avoid back fire and to protect the pump from exhaust gas. Altogether, the Secondary Air Injection Pump is crucial for emissions regulations and better fuel economy in Buick Century automobiles.
Each OEM Buick Century Secondary Air Injection Pump we offer is competitively priced and comes with the assurance of the manufacturer's warranty for the part. Furthermore, we guarantee the speedy delivery of your orders right to your doorstep. Our hassle-free return policy is also in place for your peace of mind.
Buick Century Secondary Air Injection Pump Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: How to Remove,Install and Service the Secondary Air Injection Check Valve and Secondary Air Injection Pump on Buick Century?A:The Air Management System (AMS) introduces extra oxygen after exhaust gasses through the combustion chamber are ejected and works similarly to the AIR system. Located upstream the exhaust port is an engine-driven air pump sending air into the exhaust ports or manifolds or catalyst; the air pump works always, temporarily by-passing air through the Air Management Valve during deceleration and high speed; there is a check valve preventing back flow of exhaust. This system cuts HC and CO emission by opening the exhaust ports to the air intake during cold engine operation and help the Catalytic Converter to heat up quickly. During the warm up the air is supplied to the beds of the catalytic converter in order to reduce the level of HC and CO and, at the same time, the oxygen level remains low in the first bed for accurate reduction of NOx. The ECM controls air intake to include air to the air cleaner or atmosphere depending on the engine temperature and operating condition to avoid back firing during deceleration. Normal inspections of the check valves and hoses to look for formation of leaks, cracks or deterioration must be made. For removal and installation of the air pump, one has to loosen the V-belt adjuster bolt-The belt has to be removed-Unscrews the mounting bolts, and for installation, do the reverse while ensuring the belt tension is correct. The check valve consists of removing the check valve line from the pump assembly then removing the check valve from the air injection pipe, the reverse of how it is fitted. For the Air management valve, one has to disconnect the negative cable, take off the air cleaner, tag and disconnect the hoses and air management valve bolts and reassemble the air management valve in the reverse procedure.