My Garage
My Account
Cart
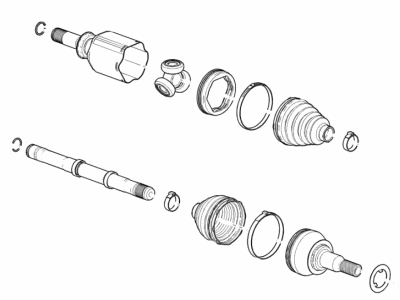
Genuine Cadillac CV Boot
Axle Boot- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
74 CV Boots found
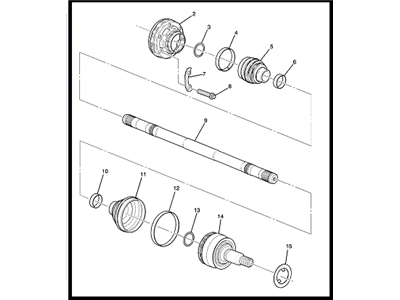
Cadillac Boot Kit,Front Wheel Drive Shaft Cv Joint
Part Number: 19256071$108.04 MSRP: $186.34You Save: $78.30 (43%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Outer Boot
- Position: Front
- Replaces: 15868187, 26069246
Cadillac Boot Kit,Front Wheel Drive Shaft Tri, Pot Joint
Part Number: 19256072$49.14 MSRP: $83.25You Save: $34.11 (41%)Product Specifications- Other Name: BOOT KIT, Front Axle; Inner Boot
- Position: Front
Cadillac Boot Kit,Front Wheel Drive Shaft Cv Joint
Part Number: 15868188$65.41 MSRP: $111.85You Save: $46.44 (42%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: BOOT KIT, Front Axle; Inner Boot, Outer Boot
- Position: Front
- Replaces: 26062619
Cadillac Boot Kit,Front Wheel Drive Shaft Cv Joint
Part Number: 19209166$52.44 MSRP: $86.77You Save: $34.33 (40%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: BOOT KIT, Front Axle; Inner Boot, Outer Boot
- Position: Front
Cadillac Boot Kit,Front Wheel Drive Shaft Cv Joint Outer
Part Number: 22833444$43.49 MSRP: $73.71You Save: $30.22 (41%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: BOOT KIT, Rear Axle Universal Joint; Outer Boot
- Position: Front Outer
- Replaces: 13291734
Cadillac Boot Kit,Front Wheel Drive Shaft Cv Joint
Part Number: 19210864$39.70 MSRP: $68.46You Save: $28.76 (43%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: BOOT KIT, Front Wheel Drive Axle Shaft
- Position: Front
- Replaces: 15918509, 19206498
Cadillac Boot Kit, Front Wheel Drive Shaft Tri, Pot Joint
Part Number: 20846096$37.34 MSRP: $61.79You Save: $24.45 (40%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: BOOT KIT, Front Wheel Drive Axle Shaft; Inner Boot
- Position: Front
Cadillac Boot Kit,Front Wheel Drive Shaft Tri, Pot Joint
Part Number: 19209167$43.56 MSRP: $75.13You Save: $31.57 (43%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: BOOT KIT, Front Axle; Inner Boot, Outer Boot
- Position: Front
Cadillac Boot Kit, Front Wheel Drive Shaft Cv Joint
Part Number: 20846097$37.34 MSRP: $61.79You Save: $24.45 (40%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: BOOT KIT, Front Wheel Drive Axle Shaft; Outer Boot
- Position: Front
Cadillac Boot Kit, Rear Wheel Drive Shaft Inner Cv Joint
Part Number: 20894127$40.35 MSRP: $66.80You Save: $26.45 (40%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: BOOT KIT, Rear Axle Universal Joint; Inner Boot
- Position: Rear Inner
Cadillac Boot Kit,Rear Wheel Drive Shaft Outer Cv Joint
Part Number: 19260857$6.74 MSRP: $10.75You Save: $4.01 (38%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: BOOT KIT, Rear Axle Universal Joint; Outer Boot
- Position: Rear Outer
Cadillac Boot Kit, Front Wheel Drive Shaft Tri, Pot Joint
Part Number: 20984614$36.36 MSRP: $92.67You Save: $56.31 (61%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: BOOT KIT, Front Wheel Drive Axle Shaft; Boot, Boot Kit, Inner Boot, Inner CV Joint Boot
- Position: Front
Cadillac Boot Kit,Front Wheel Drive Shaft Tri, Pot Joint
Part Number: 88957225$63.99 MSRP: $95.95You Save: $31.96 (34%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: BOOT KIT, Front Wheel Drive Axle Shaft; Inner Boot, Inner CV Joint Boot
- Position: Front
Cadillac Boot Kit, Front Wheel Drive Shaft Cv Joint Outer
Part Number: 13291737$45.52 MSRP: $78.49You Save: $32.97 (43%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: BOOT KIT, Front Wheel Drive Axle Shaft; Boot, Outer Boot
- Position: Front Outer
Cadillac Boot Kit, Front Whl Drv Shf Tri, Pot & Cv Jt
Part Number: 84631804$43.25 MSRP: $106.00You Save: $62.75 (60%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Boot Kit
- Position: Front
- Replaced by: 42905407
Cadillac Boot Kit,Front Wheel Drive Shaft Tri, Pot Joint
Part Number: 26075585$42.98 MSRP: $105.31You Save: $62.33 (60%)Product Specifications- Other Name: BOOT KIT, Front Wheel Drive Axle Shaft; Inner Boot
- Position: Front
Cadillac Boot Kit, Rear Wheel Drive Shaft Cv Joint
Part Number: 84150161$29.22 MSRP: $48.38You Save: $19.16 (40%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Boot Kit, Rear Whl Drv Shf Cv Jt; Outer Boot
- Position: Rear
Cadillac Boot Kit, Front Wheel Drive Shaft Cv Joint Inner
Part Number: 20920176$47.28 MSRP: $78.23You Save: $30.95 (40%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: BOOT KIT, Front Wheel Drive Axle Shaft; Boot, Inner Boot
- Position: Front Inner
- Replaces: 13291745
Cadillac Boot Kit, Front Wheel Drive Shaft Inner
Part Number: 84210421$33.03 MSRP: $51.96You Save: $18.93 (37%)Product Specifications- Other Name: Boot Kit, Front Whl Drv Shf Inr; Inner Boot, Inner CV Joint Boot, Outer Boot
- Position: Front Inner
Cadillac Boot Kit, Rear Wheel Drive Shaft Tri, Pot Joint
Part Number: 25782407$52.52 MSRP: $82.64You Save: $30.12 (37%)Product Specifications- Other Name: BOOT KIT, Rear Axle Universal Joint; Inner Boot, Outer Boot
- Position: Rear
| Page 1 of 4 |Next >
1-20 of 74 Results
Cadillac CV Boot
For superior quality and affordable Cadillac CV Boots, consider our website. We proudly present a wide selection of genuine Cadillac CV Boots at unbeatable prices. These OEM parts, supported by the manufacturer's warranty, are also eligible for our hassle-free return policy and swift delivery service.
Cadillac CV Boot Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: How to check the shock absorbers and CV Boot on Cadillac CTS?A:To check the shock absorbers, park the vehicle on level ground, turn off the engine, and set the parking brake, ensuring tire pressures are correct. Push down on one corner of the vehicle and release it, observing that it should stop moving and return to a level position within one or two bounces; if it continues to move or fails to return, the shock absorber may be worn or weak. Repeat this check at the other corners, then raise the vehicle and support it securely on jackstands. Inspect the shock absorbers for fluid leakage, noting that a light film is not concerning, but any significant leakage requires replacement of the shocks as a set. Ensure the shocks are securely mounted and undamaged, checking for damage and wear on the upper mounts, and replace them as a set if necessary. For the steering and suspension, check tires for irregular wear and proper inflation, inspect the universal joint between the steering shaft and gear housing for lubricant leakage, and ensure dust boots are intact. Examine tie-rod ends for excessive play and look for loose bolts or damaged components. While an assistant turns the steering wheel, check for free movement and binding in the steering components. Test balljoints for wear by prying the control arms up and down; any play indicates a worn balljoint that needs replacement. Inspect balljoint boots for damage and leaking grease, and at the rear, check suspension arm bushings for deterioration. For the rear CV Boots, which protect the constant velocity joints, wash them with soap and water to prevent premature deterioration from oil and grease, and inspect for tears, cracks, and loose clamps; any evidence of damage or leaking lubricant necessitates replacement.