My Garage
My Account
Cart
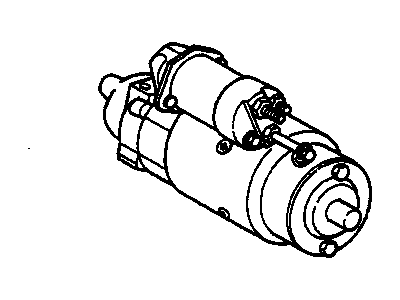
Genuine GMC Sonoma Starter
Starter Ignition- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
17 Starters found
GMC Sonoma Starter, (Remanufacture) *Use Starter
Part Number: 10465167$179.74 MSRP: $356.46You Save: $176.72 (50%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysGMC Sonoma Starter (Remanufacture)
Part Number: 10465577$328.66 MSRP: $595.83You Save: $267.17 (45%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysGMC Sonoma Starter, (Remanufacture)
Part Number: 10465490$86.89 MSRP: $263.51You Save: $176.62 (68%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysGMC Sonoma Starter Asm, (Remanufacture) (Pg260D)
Part Number: 89017637$335.20 MSRP: $666.37You Save: $331.17 (50%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysGMC Sonoma Starter Asm, (Remanufacture Pg260D)
Part Number: 89017714$254.20 MSRP: $504.88You Save: $250.68 (50%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysGMC Sonoma Start Motor Assembly (Remanufacture)
Part Number: 10465459$112.35 MSRP: $339.90You Save: $227.55 (67%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysGMC Sonoma Motor Assembly, Start
Part Number: 10455053$86.89 MSRP: $263.51You Save: $176.62 (68%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysGMC Sonoma Starter Asm, (Remanufacture) (Pg260G)
Part Number: 89017441$259.32 MSRP: $487.51You Save: $228.19 (47%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysGMC Sonoma Starter, (Remanufacture)
Part Number: 10465065$173.94 MSRP: $315.30You Save: $141.36 (45%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysGMC Sonoma Motor, Starter (Remanufacture) (Sd205)
Part Number: 10465434$110.71 MSRP: $197.64You Save: $86.93 (44%)
GMC Sonoma Starter
It is a starter motor with great importance for the GMC Sonoma, as this part is responsible for starting the operation of the vehicle's engine with the help of converting the electrical energy of the battery into mechanical energy. This process starts by turning on of the ignition key which in return switches on the solenoid of the starter and as a result connects the start drive gear with the fly wheel of the engine. This GMC Sonoma starter is an armature type with gear reduction and helps the starting process by engaging the armature with the drive through a reduction gear. This setup has the greatest advantage when it comes to the dynamic processes that involve the sudden calls of starting the engine. It cannot be determined what types of starters the GMC Sonoma may have used over the years, though additional information which may have described various models or frequency adjustments were not included. In general, enlargements may comprise the so-called gear-reduction gadgets, which are known to generate high torque at slow speeds, as it is necessary for starting high-compression engines. This is especially so for performance engines or high alter engines where standard OE (original equipment) starters may not adequate since they lack sufficiently high output torque and often the correct timing also. Some tips pertains to the maintenance of the starter includes checking that all cables including the battery cables are firmly secured and free from corrosion so that there will not be any electrical problems when cranking a GMC Sonama. It is suggested to test the GMC Sonoma starter during the vehicle upkeep and maintenance so that it would function effectively and consistently, and that the performance of the starter should be at its peak.
Each OEM GMC Sonoma Starter we offer is competitively priced and comes with the assurance of the manufacturer's warranty for the part. Furthermore, we guarantee the speedy delivery of your orders right to your doorstep. Our hassle-free return policy is also in place for your peace of mind.
GMC Sonoma Starter Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: How to troubleshoot a starter motor that does not turn when the switch is operated on GMC Sonoma?A:If the starter motor does not turn when the switch is operated, first check the shift lever (for automatic transmission) or clutch pedal (for manual transmission). Ensure the battery is charged and all cables are securely connected. If the motor spins but the engine does not crank, the starter motor may need to be replaced. If the solenoid clicks but the motor does not operate, the issue may be with the battery, solenoid contacts, or starter motor. If the solenoid plunger cannot be heard, it may be defective or there may be an open circuit. To check the solenoid, connect a jumper lead between the battery and "S" terminal. If the motor operates, the solenoid is fine. If not, remove the starter/solenoid assembly for testing and repair. If the motor cranks slowly, check the battery and terminal connections. If the engine is partially seized or has the wrong oil, it may crank slowly. To diagnose further, run the engine until normal temperature, then stop and disconnect the coil wire. Connect a voltmeter to the starter motor terminal and ground. Crank the engine and take voltmeter readings. A reading of 9 volts or more at normal cranking speed is normal. If the reading is less than 9 volts and the cranking speed is slow, the solenoid contacts may be burned.